
Mid-size or large businesses need to manage a massive amount of data. This includes employee data, user credentials, business reports, logs for auditing and compliance. If you are a banking or an e-commerce website, this may include transaction data, customer reviews, internal files, etc. Can businesses store all this data on its backend on-premise servers? Technically, you can, but judiciously, you shouldn't.
Why? On-premise servers add up the infrastructure and maintenance costs. For example, SQL Server for your relational data needs and a MongoDB Server for your unstructured data, etc. Also, if unaware of the amount of data ingestion, businesses might end up setting up low or high storage, thereby experiencing scalability issues. Moreover, disaster management is something that adds an overhead cost to your enterprise.
So, how about getting insights on the key services, features offered by Azure Storage? In addition to understanding the replication solutions, and the seamless migration needs without compromising on the integrity, security and maintenance of your data. In this blog series, we will look at Microsoft Azure that offers this service.
Microsoft Azure Storage: By the Numbers
Azure Storage platform is a one-stop shop for all your storage requirements. From storing large structured and unstructured binary data, looking for a cloud accessible file share, to developing an asynchronous application which might require a messaging queue, and for many other use case scenarios, Microsoft Azure Storage helps businesses to store, secure and manage their data.
The growth of Microsoft Azure in the market is exponential as compared to its competitors. Microsoft Azure revenues grew 62% in the Q4 2019. Microsoft's earnings report beat analysts' expectations with revenues of $36.9 billion (up 14%), and a net income of $11.6 billion (up 38%). Over 95% of Fortune 500 companies use Microsoft Azure for their use cases and comparatively, the service is budget-friendly. However, let’s deep dive and explore the service in detail.
In this first part of the blog series, we will explore Storage Account, the services offered, features and Performance Tiers of Microsoft Azure Storage. In the second part, we will look at the various types of Storage Accounts, Blob Access Tiers, Storage Account Replication, Security and Pricing.
Storage Account:
In Microsoft Azure Storage, a Storage Account is a unique namespace to the data you store. It stores different kinds of data such as blobs, files, tables, queues, etc. Besides, it gives you a base address to access your data.
A Storage Account is divided into two planes:
- Management Plane: This is where you manage the configurations of your storage account. It is with the rules and policies that you define to manage your storage account. A set of features offered by Microsoft Azure to perform tasks such as creating a container, setting up firewall policies, setting up private endpoints, etc.
- Data Plane: In Microsoft Azure Storage, a data plane is where the actual data is contained, such as your blobs are at the data plane level. Businesses can configure various rules, policies and security measures to manage access to your data plane using the management plane.
Services Offered by Microsoft Azure Storage
Microsoft Azure offer the below mentioned key services. Let’s find out the function of each service and its relevance in a business use case.
Azure Blob Storage: In Microsoft Azure Storage, BLOB stands for Binary Large Objects. It allows you to store huge unstructured data; the data that does not adhere to a particular structure such as text files, binary files, video files, etc. Mostly, Azure blobs are used for random access, but maybe not frequent.There are three types of blob storage:
- Block Blobs:
Block blobs store information in blocks. It is primarily used for text and binary data. It has a maximum space of 4.7 TB
- Append Blobs:
Append blob allows the addition of new blobs to the existing blobs. For example, you may have a log file that is continuously being appended by new logs.
- Page Blobs:
Page blobs are used to store random access files of a maximum of 8 TB. A virtual hard disk can be stored in page blobs and are used as disks for virtual machines.
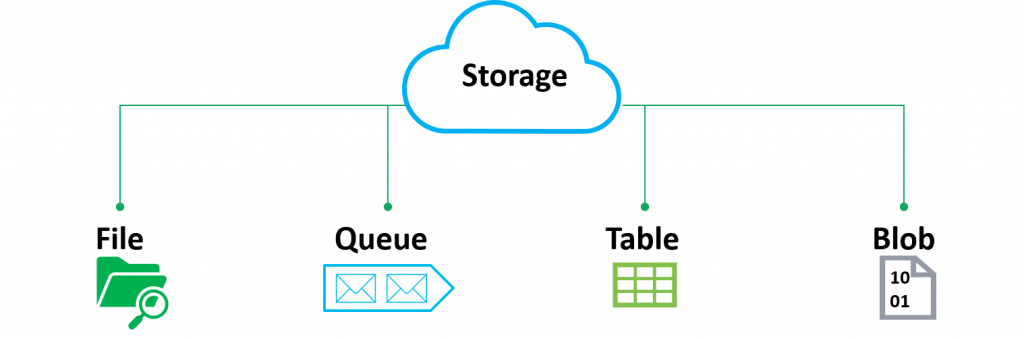
File Storage: In Microsoft Azure Storage, File storage acts as a network shared drive on Azure. It uses SMB protocol just as in the on-premises environment. You can mount Azure Files on-prem using Azure File Sync. This approach helps you to use your on-premises file server as a cache server. The service of File storage is useful in lift and shift scenarios.
Queue Storage: Businesses can use Queue storage to store a large number of messages to process asynchronously. The service can be used to create a backlog of work and allows the decoupling of applications.
Table Storage: In Microsoft Azure Storage,Table storage is used for structured non-relational data. It is a NoSQL data store.
Data Lake Storage: This is based on Azure Blob storage. Blob storage does not give a hierarchical structure to your files and folders. However, Data Lake storage does that for you. It is a big data analytics solution by Microsoft.
Important Features of Microsoft Azure Storage:
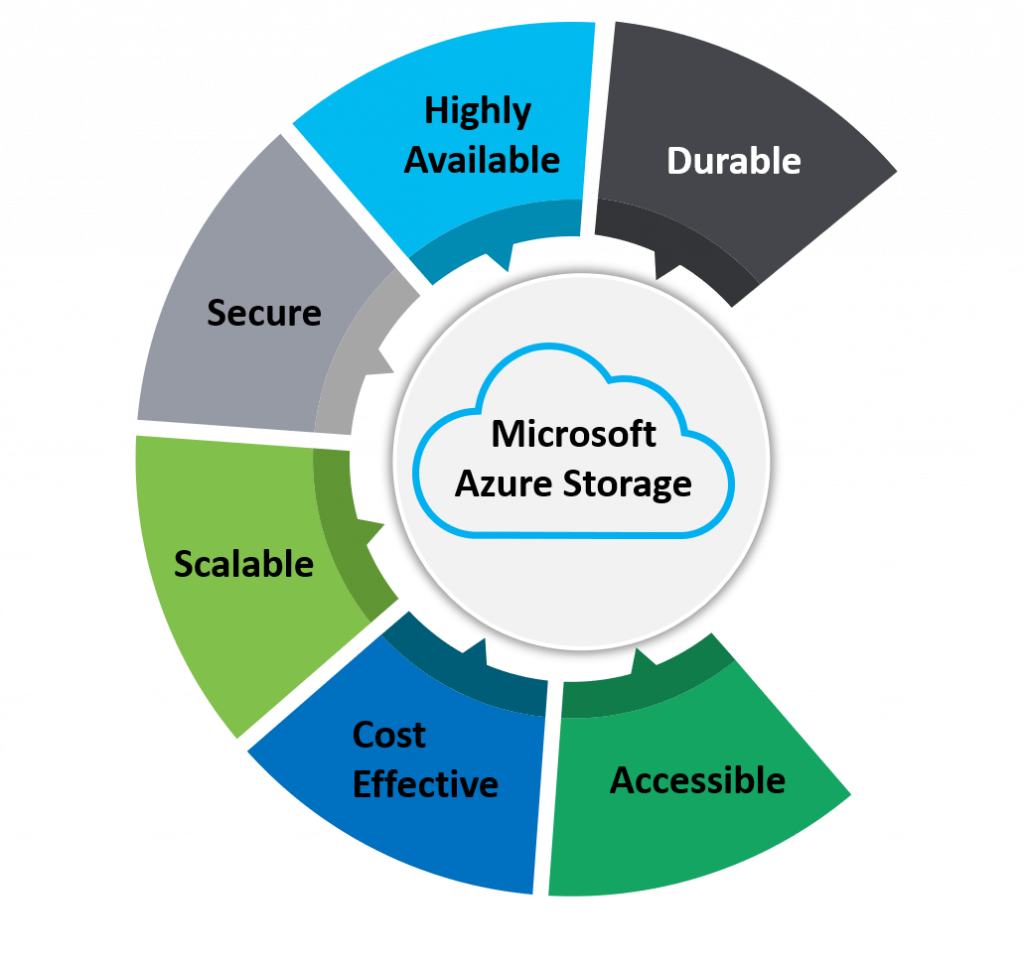
Whenever a client uses cloud storage as a solution, it is mandatory to ensure safety and availability of the client's data. The storage system should be able to handle any sudden rise in traffic and should be ready for any kind of adversities.
Below are the features of Azure Storage:
- Availability: Microsoft Azure has multiple data centers spread across various geographical regions and Content Delivery Networks, for example, North America. The service assures that your application data is available to your customers anytime and prevents any latency in serving your customers.
- Scalability: Being cloud storage, an enterprise does not have to add any new servers manually to address your surge or ebb in user requests. Scalability is taken care of by Microsoft Azure as per your need.
- Security: Clients have doubts regarding sharing their data with a cloud provider. Microsoft Azure offers various features, such as encrypting data at rest or in transit. You can administer various policies to prevent any unauthorized access to your storage account and provide fine-grained authorization rights to a user. To keep your data secured, you can set specific roles and also features such as Storage Account Keys and Shared Access Tokens.
- Managed: Businesses need not worry about the underlying infrastructure for storage. Microsoft Azure manages all by itself. Besides, regular patches and software updates are provided by Microsoft Azure.
- Accessibility: In Microsoft Azure Storage, there are various ways to access your storage accounts on Microsoft Azure. These are via Azure portal, PowerShell, Azure CLI, SDKs and Rest APIs for developers, etc.
Performance Tiers:
Microsoft Azure Storage offers two types of performance tiers:
- Standard: Standard performance tier gives your business high capacity and high throughput.
It supports most of the storage services.
- Premium: Premium performance tier gives your business high transaction rate and consistent storage latency.
Stay tuned for our next part of the blog. You will explore the types of Storage Accounts, Blob Access Tiers, Storage Account Replication, Security and Pricing. Also, we will look briefly look into a couple of use cases for businesses.
Want to know how Xoriant can help you with Microsoft services? Explore our Microsoft Partnership here.
Connect with our experts if you are you looking to adopt Microsoft Azure services into your existing software applications.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/common/storage-account-create?tabs=azure-portal



 View Previous Blog
View Previous Blog