
Statista projects the Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM) market to cross the USD 3 billion mark in a couple of years, double the value it constituted in 2017.1
Improved ROI (35%), internal communication (47%), employee satisfaction (23%), and employee loyalty (21%) remain the major drivers for the growth of enterprise mobile application development.2
With new and improved features such as WebGL, HTML5 Canvas (including 3D graphics), CSS3 animations, and even video game development libraries like Unity being available, developers and designers are creating richer interfaces with less hassle. However, new capabilities introduce challenges in mobile application testing that are unique from desktop-focused testing. For instance, key features of HTML5, including jiggle elements and animating GIFs alongside WebGL, WebRTC, and CSS3 animations, all come with their own quirks.
Enterprise mobile applications also run on different operating systems, which complicates the development process, for the goal is to build an enterprise mobile application that facilitates cross-platform compatibility.
This makes it imperative to understand the latest trends in mobile testing methods and explore the avenues for the implementation of an effective mobile app testing strategy.
The Ever-Changing Landscape of Mobile Testing
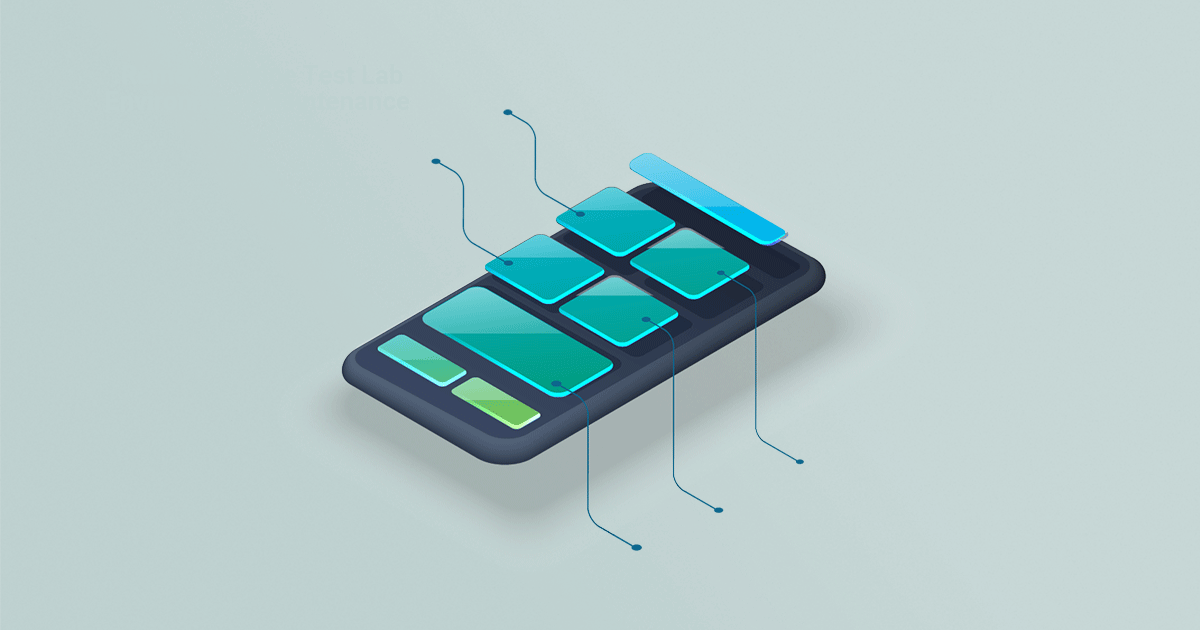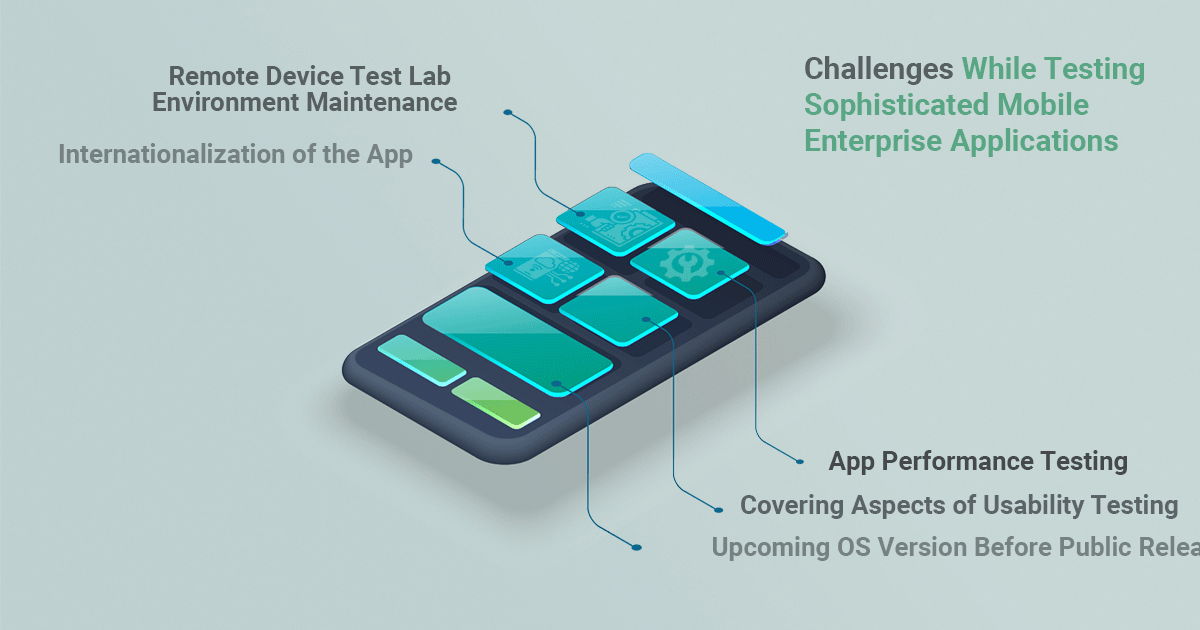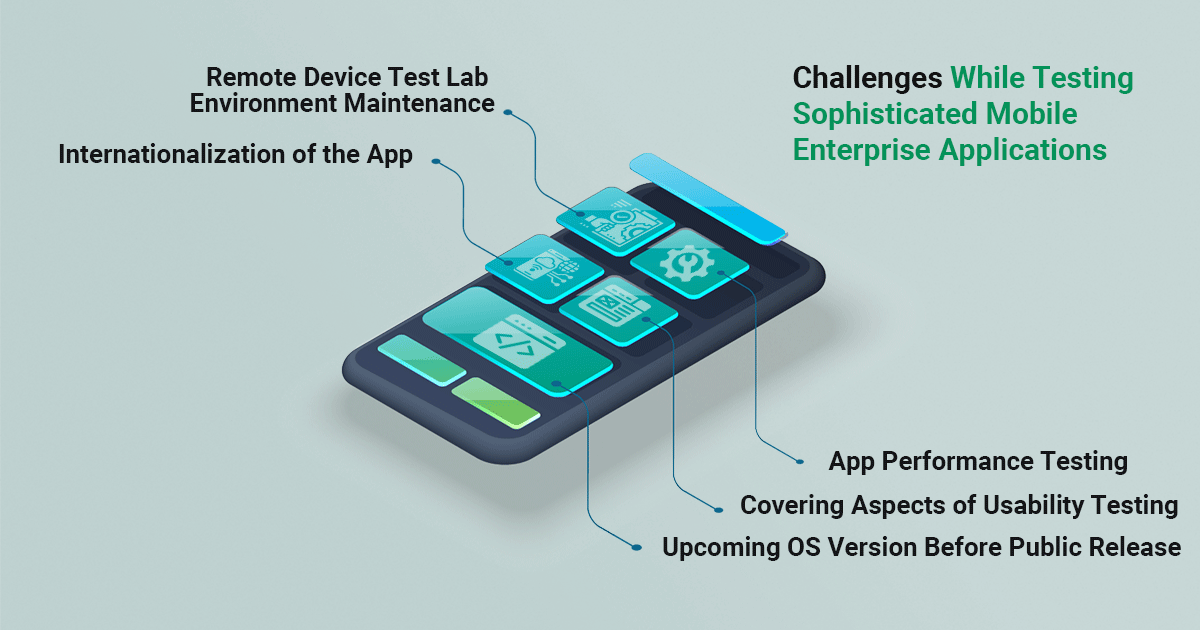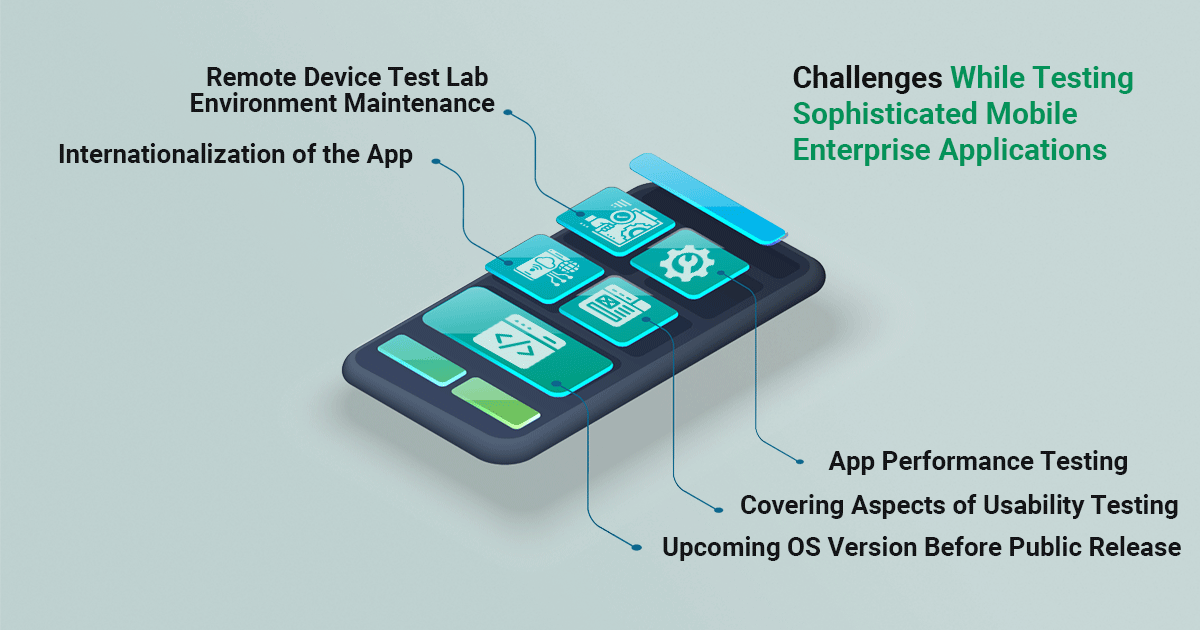
Challenges While Testing Sophisticated Mobile Enterprise Applications
From identifying the QA challenges in mobile application testing tools to ensuring security and maintaining on-premise device labs to delivering robust applications — a host of challenges confront the ISVs looking to test mobile apps.
Here are the five biggest technical challenges:
1. Coping Up with Upcoming OS Version Before Public Release
A common challenge faced by enterprise mobile applications for both iOS and Android is the lack of preparedness regarding the upcoming OS version. In most cases, a developer or the enterprise might release the app on the new OS as soon as it is made available. This approach often results in several bugs that come to light only when the app hits the market.
On top of this, since enterprises often tend to focus more on the mobile application development of features rather than testing, they end up neglecting certain aspects such as UX, impacting the new features introduced in the OS affecting app functional flow and security standards. In some ways, this is a consequence of the ISV’s disproportionate focus on the desktop app over the mobile app.
2. Covering Aspects of Usability Testing
The end-users are conditioned by the enterprise mobile apps they use in every other aspect of their life. Their expectations of the enterprise apps are high too. This makes it hard for ISVs to provide users with 'application assistance' throughout their journey. This must be done through usability testing, and this process is becoming more and more important as ISV try to develop products that enterprise employees (their end-users) will love to use.
Using native tools, it is possible to test for the usability of enterprise mobile applications, but these tools are costly and often impractical. There is also a lack of ready-made tools and SDKs for different platforms. This kind of testing comes down to nuance and judgment, the domain of the expert usability tester.
3. Accessing – And Maintaining – Remote Device Test Lab Environment
There is a severe shortage of devices for periodic testing that could be used to validate application features, in particular. More and more devices get released. The capabilities of these devices, their inherent capabilities, form factors, and utilities all keep evolving. It’s only apt that the enterprise mobile applications tap the full capabilities of these devices. But it becomes a logistical nightmare to build a test lab with enough devices to test the range of options. Given the rate of technology obsolescence in this space, maintaining the lab is also a massive challenge.
4. App Internationalization
Perhaps the biggest challenge that ISVs with a global footprint face is the facilitation of a seamless application that meets customer expectations in disparate markets and conditions. Enterprise mobile app development localization and internationalization is an important parameter to be considered by the engineering teams.
ISVs find it difficult to manage the changes in user experience in different languages and customizations. They must also allow for variations in telecom networks, security standards, and user behavior across locations. One example of app internationalization is supporting right to left written languages, such as Arabic. Here it is not only about displaying translated strings but managing the app content right aligned. In fact, in this case, the entire application should be mirrored.
5. App Performance Testing
Several factors decide an enterprise mobile app's performance, including the network connection, screen response time, battery consumption, and the device itself, on the whole. For instance, a low-end tablet with limited RAM could adversely affect an enterprise application's performance.
Mobile apps deal with data, and the throughput of data, the efficacy of data rendering, and the conditions that address data load (and overload) are important to consider too. For ISVs looking to provide enterprises with apps that meet user expectations, it becomes important to create comprehensive performance testing strategies that address all these complexities.
Key Enterprise Mobile Application Testing Trends in 2021
1. API and Service Testing
The rise of cloud services and APIs can drive significant evolution. These technologies, along with the emergence of native cross-platform app development, reduce the need for a range of enterprise mobile app testing tools. Cloud-based mobile app testing, cloud-based application security testing tools, cloud penetration testing
2. Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) Testing
With Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) being a need than a choice, enterprise mobile apps can now be tested without having access to the device's software and hardware, along with a DSLR camera for UX and UI testing.
3. Script-less Test Automation
The adoption of Low-code or no-code by engineering teams is on the rise for the accelerated delivery of enterprise applications. Engineering teams are minimizing maintenance with scriptless testing automation. Testing tools have matured beyond script-based platforms and the adoption of script-less test automation will amplify.
4. Real Device Cloud Testing
With the emergence of cloud services and APIs to empower rapid mobile development updates, enterprises can now accelerate their testing by leveraging a range of cloud device options.
Important Factors to Consider for Enterprise Mobile Application Testing
In the context of enterprise mobile apps, multiple features demand diverse testing standards. Needless to say, all features should be thoroughly tested before being deployed into the production environment. Here are some factors to consider for enterprise mobile application testing:
- Determine the scope of mobile enterprise apps and embrace reusable code.
- Use JavaScript to manipulate the DOM or change elements in different ways across all platforms, as well as across multiple mobile browsers.
- Leverage the latest mobile device emulators and other tools that mimic real devices to test your applications on multiple platforms and mobile devices.
- Use mobile application testing tools to ensure your enterprise mobile apps are performing the way you want them to.
- Use test automation to help increase the speed and coverage of your testing efforts.
- Maintain a realistic budget and remember to allocate adequate time for mobile testing.
- Document all test cases, and ensure that every bug is properly documented before it is fixed.
- Develop your mobile app testing plans by leveraging the capabilities and experience of an enterprise mobile application development and testing expert such as Xoriant.
Xoriant's Enterprise Mobile Application Testing — The Promise of Quality
Xoriant has rich experience in building enterprise applications for some of the leading ISVs in the world. We have helped many of those products enter the mobile age and achieve user success. Our robust testing and validation techniques ensure enterprise mobile applications are designed to scale and perform while being secure. Our testing frameworks, such as iPerform and iAutomate, amongst others, are designed to be robust, scalable, and flexible. Thus, contributing to increased speed and test coverage, improved test quality, and a better ROI.
Let's talk about Specialized Quality Engineering for your success!
Connect with Xoriant SQE Experts
References
Business Value of Mobile App Development 2021



 View Previous Blog
View Previous Blog